Today, despite the slowdown, China’s GDP is US$ 17.95 trillion, making it the 2nd largest economy in the world. For 2023, the Chinese government expects a 5% growth in the country’s GDP. China’s GDP per capita in 2022 is around US$12,417.64, well below the US$70,248.63 recorded in the US.
China’s GDP (Gross Domestic Product) has grown at impressive rates in recent decades, making the country a global economic powerhouse. As a result, many investors have wondered how this growth could impact their investments and whether it is worth exposing part of their portfolios to the Asian giant.
After all, the Chinese economy is strongly intertwined with the global market and influences the prices of various commodities and sectors around the world.
In this content, we will explore how China’s GDP growth can affect your investments and what investors should consider when investing in companies with exposure to the Chinese economy. Let’s go?
What is China’s GDP value today?
Before talking about the investments themselves, we need to know better what China’s GDP is and its composition. In this way, we will better understand how the 2nd largest economy in the world generates wealth.
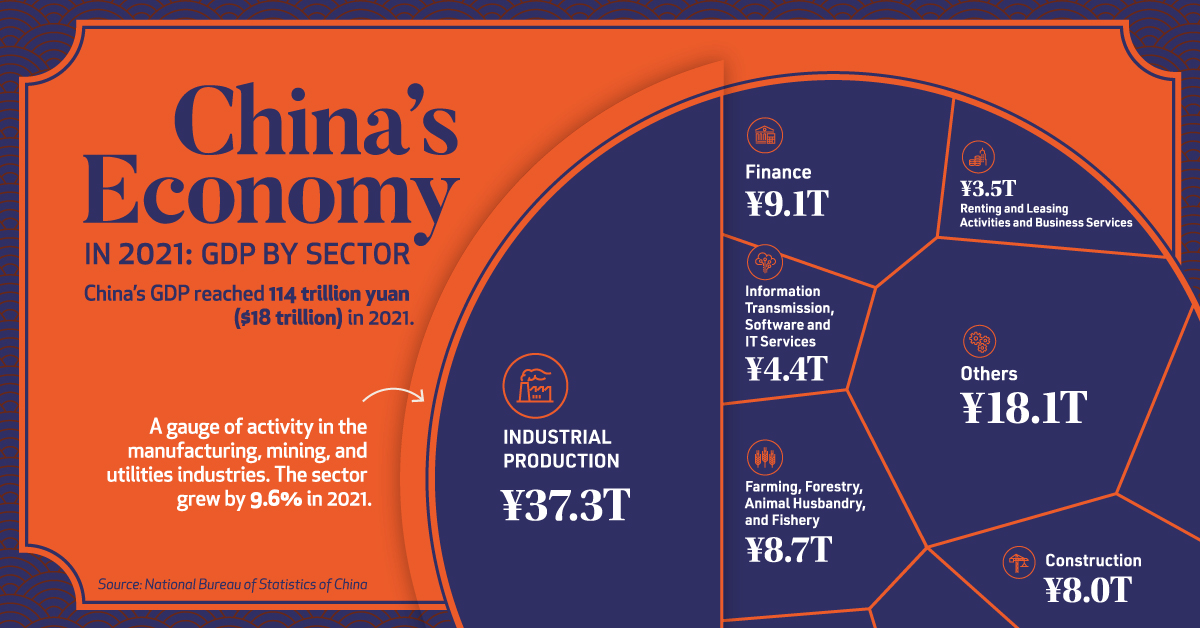
In 2022, China’s GDP grew by 3% and reached approximately US$17.95 trillion.
However, this figure was below the official target of the country’s government for the year (5.5%) and represented a major slowdown compared to 2021, when it grew 8.4%, according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China ( NBS) .
This was the second worst result in almost 50 years, second only to the 2.2% of 2020 (pandemic year), since the country was enormously impacted by the restrictive Covid-zero policy.
Added to this, the crisis in the Chinese real estate market , the cooling of the European and American economies, the contractionary monetary policies around the world, in addition to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, contributed to lower growth.
Despite the advances, China faces challenges, such as excessive dependence on the real estate sector for growth and the reversal of the age pyramid, resulting from the one-child policy.
The division of the contribution in the Chinese GDP is given by 7.3% primary industry (agriculture and natural resources from land or sea), 39.9% secondary (industry) and 52.8% tertiary (service sector).
What is China’s per capita GDP?
GDP per capita is a measure of the Gross Domestic Product of a country divided by the number of inhabitants. It is often used as an indicator of the well-being and enrichment of a country’s population, as it reflects the production of goods and services per person.
In 2022, China’s GDP per capita showed deceleration, growing by 3.0% and amounted to 85,698 yuan (about US$12,417.64), said the NBS.
Observe, in the table below, the evolution of GDP per capita in China, Brazil and the USA in recent years.
| Year | China’s per capita GDP (US$ per year) |
Brazil’s per capita GDP (US$ per year) |
US GDP per capita (US$ per year) |
| 2021 | 12,556.33 | 7,507.16 | 70,248.63 |
| 2020 | 10,408.67 | 6,794.49 | 63,530.63 |
| 2019 | 10,143.84 | 8,845.26 | 65,120.39 |
| 2018 | 9,905.34 | 9,121.08 | 62,823.31 |
| 2017 | 8,816.99 | 9,896.68 | 59,907.75 |
| 2016 | 8,094.36 | 8,680.77 | 57,866.74 |
| 2015 | 8,016.43 | 8,783.22 | 56,762.73 |
| 2014 | 7,636.12 | 12,071.16 | 55,123.85 |
| 2013 | 7,020.34 | 12,258.50 | 53,291.12 |
Source: World Bank
Why does Chinese GDP grow so much?
China’s economic growth in recent decades has been remarkable, making it the 2nd largest economy in the world.
This success is largely due to the economic reforms initiated in the 1970s, which opened the Chinese economy to the world and encouraged foreign investment.
Since then, China has adopted a market-oriented economic policy, with an emphasis on industrialization and export of manufactured goods, as well as heavy investment in infrastructure and education .
China’s abundant and relatively cheap labor has also contributed to its competitiveness in the global market. Over time, the country has become a global manufacturing center and an important destination for foreign investment.
What is the trend for China’s GDP in the coming years?
The main trend is that, even with the slowdown, and according to some projections, China should overtake the US economy in 2028, which would be 5 years below the forecast by the Center for Economic and Business Research (CEBR, in its acronym in English).
Still in Asia, India is expected to surpass Japan’s economy and start to compete even more strongly with the Chinese.
For 2023, the Chinese government has set a growth target of “about 5%” for 2023, according to Premier Li Keqiang’s government work report . The country continues to implement internal stimulus policies and investment attraction to reverse the 2022 result and boost its GDP again.
How does China influence the growth of other countries?
In the illustration above, we see that world growth depends a lot on Chinese growth, as the Chinese economy is one of the largest in the world and has a great impact on the global economy.
China is a major producer and exporter of manufactured goods such as electronics, machinery and textiles, which means that many countries rely on its production to supply their domestic markets.
Furthermore, China is the world’s largest importer of raw materials such as iron ore, copper and oil, and its consumption of these resources is an important factor in the global economy.
As a result, a slowdown or crisis in the Chinese economy could have a significant impact on financial markets and the global economy .
In short, China’s economic performance impacts countries mainly by:
-
-
- Export of manufactured goods: China is a major producer and exporter supplying markets across the world. This can stimulate the economy of other countries that depend on it to supply their domestic markets.
- Consumption of raw materials : China is the world’s largest importer of commodities such as iron ore, copper and oil. Your consumption of these resources is an important factor in the global economy, as it influences the prices and production of these goods around the world.
- Foreign investments : it is an important destination for investments in sectors such as technology, infrastructure and energy.
- Currency Policy : The Chinese government maintains tight control over its currency policy, which can influence exports and imports from other countries.
- Infrastructure Investments : Invest heavily in infrastructure around the world, especially in developing countries.
- Integration into the global economy : China has integrated into the global economy in a number of ways, including its joining the World Trade Organization and signing trade agreements with other countries.

-
How does the evolution of China’s GDP affect your investments?
Sustained growth in the Chinese economy can boost global trade and spur growth in other countries. For these reasons, many investors, companies and governments are paying close attention to the performance of the Chinese economy and its impact on the world economy.
For Brazilian investors, the evolution of China’s GDP has the following impacts:
- Commodities : valuation or devaluation of raw materials and the shares of the companies that sell them, such as Vale, Gerdau, Suzano, Petrobras, among others.
- China Exposure : Creating strategies to take advantage of Chinese companies through ETFs and BDRs.
- Currency Exchange : Currency policy and economic performance can also impact the value of various currencies and the performance of Exchange Funds around the world.
- Consumer market : billions of people to consume products exported by Brazil.
- World growth : the advancement of the Chinese economy is favorable for the growth of several companies around the world.
Therefore, it is important for individual investors to follow the evolution of China’s GDP and other economic indicators to assess opportunities and risks in their investments.
How to expose your portfolio to China’s GDP growth?
For those who want to expose part of their capital to investments in China, the main alternatives are:
- Investment Funds : the first alternative is to look for international Investment Funds that invest in Chinese stocks or other assets.
- ETF XINA11 : Another option is to invest in ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) that track Chinese stock indices, such as the XINA11, which replicates the MSCI China index and has a management fee of 0.30% per year.
- BDRs (Brazilian Depositary Receipts) : share receipts issued in Brazil that represent shares of foreign companies, and can be acquired on the B3 (Brazilian Stock Exchange).
- ADRs (American Depositary Receipts) : stock receipts issued in the US and representing shares of foreign companies.
- Stocks recommended by Toro : recommendation from our Analysts of 5 Brazilian stocks that can appreciate a lot with the reopening of China.
Remembering that the assets mentioned above are not purchase recommendations nor do they necessarily express the opinion of Toro Analysts.
It is important to remember that investing in Chinese stocks involves risks, such as market risk, currency risk and political risk, as discussed above.
Therefore, in addition to good portfolio diversification , it is essential to carry out a careful analysis of the companies and sectors in which you intend to invest, in addition to having the help of a professional specialized in investments such as Toro’s Advisors, who are prepared and available to help you.
